Multicellularity, Development, and Reproduction Organismal Biology
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism. All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social amoebae such as the genus Dictyostelium.

PPT Multicellular Organisms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2282677
Conclusion. Cells are the smallest common denominator of life. Some cells are organisms unto themselves; others are part of multicellular organisms. All cells are made from the same major classes.
Multicellular Organisms
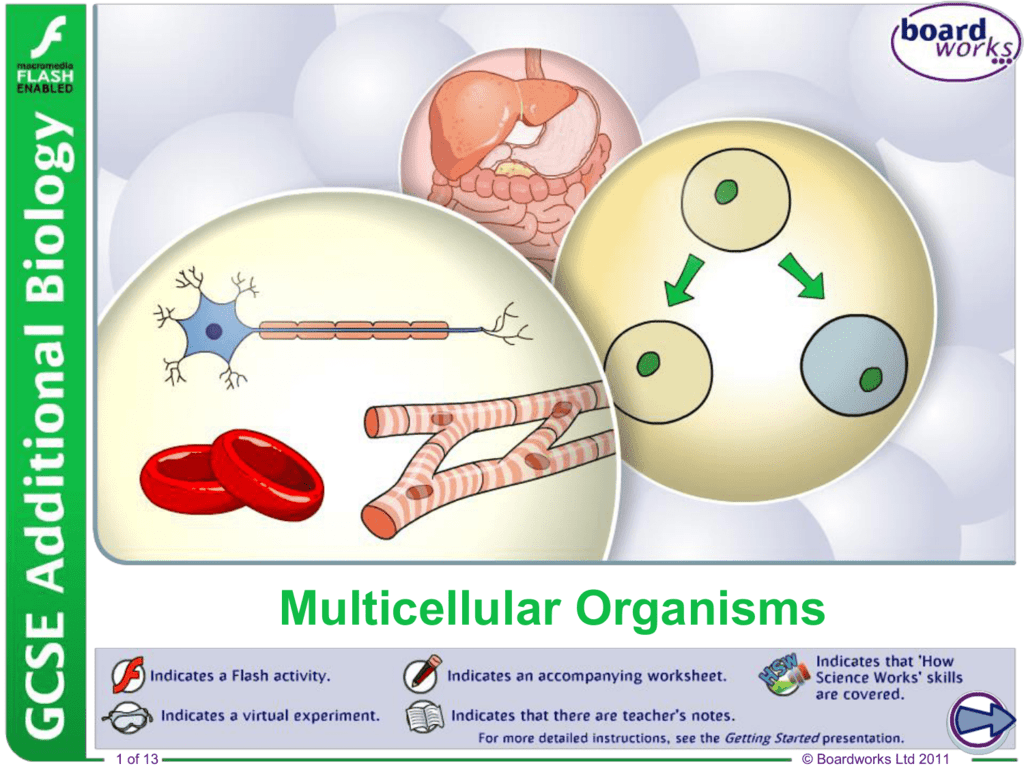
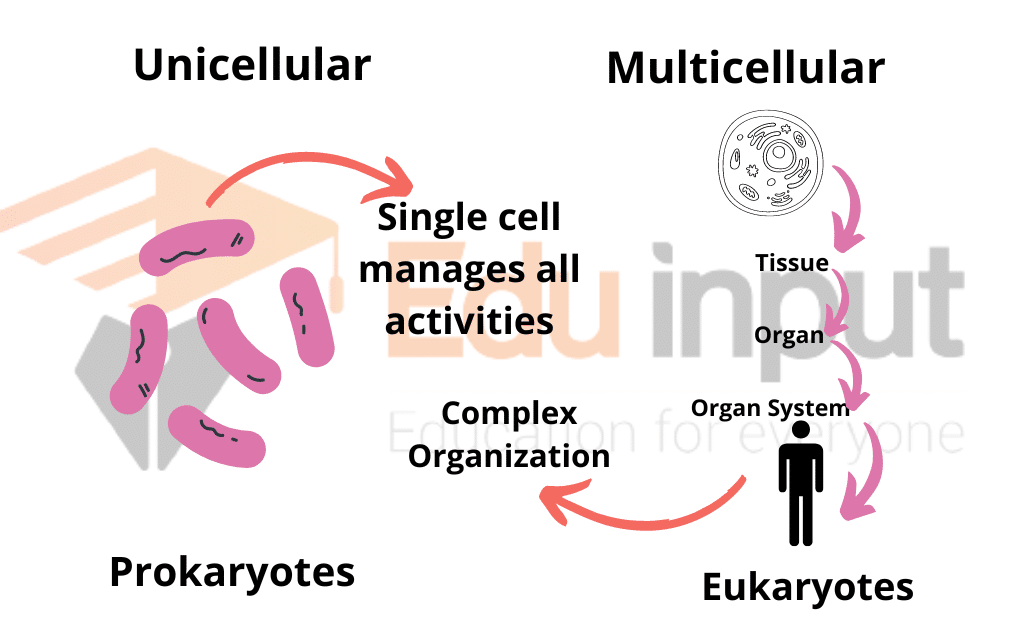
Organization of multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical structural organization, in which any one system is made up of numerous parts and is itself a component of the next level. Created by Sal Khan.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/multicellularGE-57d812963df78c58333ff5c0.jpg)
The 8 Main Characteristics of Animals
Life - Multicellularity, Evolution, Adaptation: Since multicellularity evolved independently in every major group of microorganisms, the blurred distinction between single-celled and many-celled organisms has become obsolete. The protists are divisible into about 35 unambiguous groups called phyla. They provide many examples of biological principles—including the prevalence of independent.
Multicell Organisms
Cells and organisms are the basic units of life. In this article, you will learn about the structure, function, and diversity of cells and organisms, and how they interact with their environment. Khan Academy is a free online platform that offers courses in various subjects, such as math, science, art, and more. Join us and discover the amazing world of cells and organisms.

Multicellular and Unicellular Organisms Differences and Examples
Grand Evolutionary Transitions: The eruption of multicellularity. Around 600 million years ago, single-celled life transitioned to multicellular life forms, begetting a paradigm shift in the definition of life on earth. This was an event so remarkable in earth's timeline that it would set the stage for the evolution of complex organisms, from.

PPT Multicellular Organisms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9650429
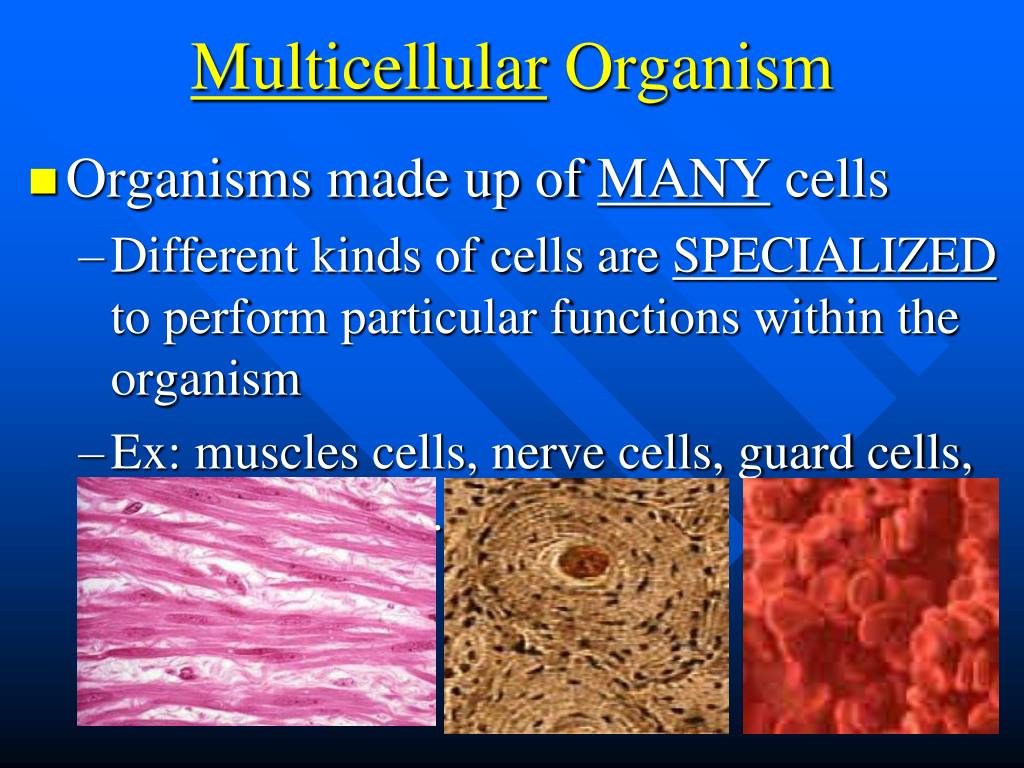
Multicellular Definition. A tissue, organ or organism that is made up of many cells is said to be multicellular. Animals, plants, and fungi are multicellular organisms and often, there is specialization of different cells for various functions. In contrast, unicellular, or single-celled organisms are much smaller in size and less complex as.

Multicellular organisms examples and characteristics Jotscroll
So, a multicellular organism definition is: an organism that is made of many cells, such as plants, animals or fungi. Multicellular organisms are different from unicellular organisms, such as.
PPT Multicellular Organisms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9650429
Development occurs following reproduction in multicellular eukaryotes. We'll switch gears now to take an overview of reproductive processes in eukaryotes, including both sexual and asexual reproduction. When organisms reproduce asexually, the offspring is an exact genetic copy of the parent.

What are multicellular Organisms Concept, functions and examples
Multicellular organisms are made of more than one cell and are complex organisms. They are visible to the naked eye. They possess distinct organs and organ systems. They are eukaryotes, i.e., they contain membrane-bound structures. Their cells exhibit division of labour. Their size increases with the number of cells in an organism.

single celled organism vs multicellular
Definition. Multicellular organisms are those composed by multiple cells. They are classified in 13 major groups of terrestrial living beings, including animals, plants, fungi, ciliates, algae, and foraminifera. The number of cells per organism range from some tens to up to several million. The cells in a multicellular organism are usually.
What Are Multicellular Organisms? Characteristics and Organization
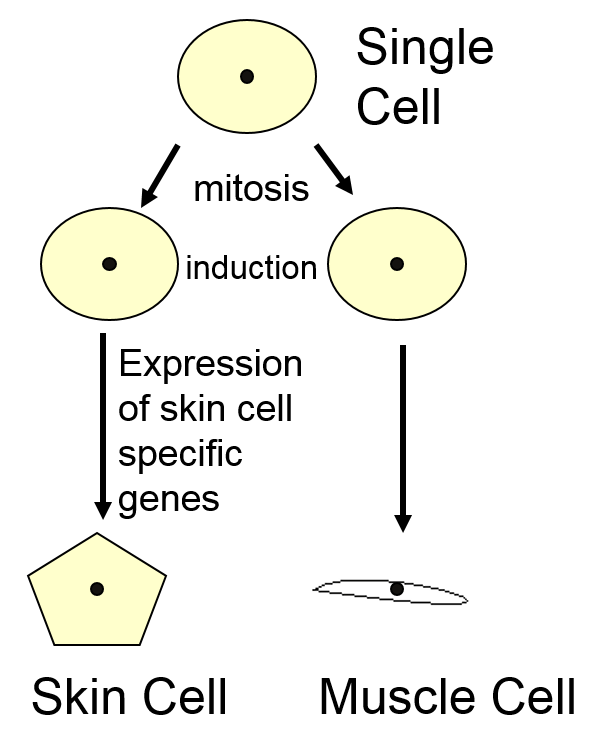
Multicellular Organisms Development. While all consist of more than one cell, they start out as a single cell. The cell proliferates to produce many more cells that result in the multicellular organism. The process starts with a single fertilized cell that increasingly divides to form many more cells. In the process, the genome causes the cells.

Multicellular organisms
Volvox is a spherical alga with about 2,000 cells and two cell types, into which the swimming and reproductive functions of the Chlamydomonas unicell have been segregated. Two things make Volvox.
PPT CELLS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2282464
Colonial Organisms. Colonial organisms were probably one of the first evolutionary steps towards multicellular organisms. Algae of the genus Volvox are an example of the border between colonial organisms and multicellular organisms.. Each Volvox, shown in Figure above, is a colonial organism.It is made up of between 1,000 to 3,000 photosynthetic algae that are grouped together into a hollow.
2.1.7 State that multicellular organisms
The cells in complex multicellular organisms like people are organized into tissues, groups of similar cells that work together on a specific task. Organs are structures made up of two or more tissues organized to carry out a particular function, and groups of organs with related functions make up the different organ systems.

Multicellular Life — Definition & Overview Expii
Figure 21-1. The four essential processes by which a multicellular organism is made: cell proliferation, cell specialization, cell interaction, and cell movement. In a developing embryo, all these processes are happening at once, in a kaleidoscopic variety of different ways in different parts of the organism. To understand the basic strategies.
- Rollo De Papel Maquina Transbank
- Account Assignment Mandatory For Material Me51n
- Acciones Para Atraer Nuevos Clientes
- C14 Panel Mount Iec Plug
- Fotos Ubicacion Soporte Motor Honda Accord 2 0
- Juego De Llaves Fijas Bahco
- Elias Torres Martinez Lapeña Arquitectos
- Mejores Universidades De Odontologia Del Mundo
- Centros De Desintoxicación Gratuitos Castilla Y León
- Ejercicios Con Cuerdas De Resistencia