
19 Fun States Of Matter Worksheets Free PDF at
A physical property is an attribute of matter that is independent of its chemical composition. Density, colour, hardness, melting and boiling points, and electrical conductivity are all examples of physical properties. Any characteristic that can be measured, such as an object's density, colour, mass, volume, length, malleability, melting.
PPT Properties of Matter PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
In each of these examples, there is a change in the physical state, form, or properties of the substance, but no change in its chemical composition. Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: (a) Wax undergoes a physical change when solid wax is heated and forms liquid wax. (b) Steam condensing inside a cooking pot is a physical change, as water vapor is changed.

What are the properties of matter? Brainly.in
The characteristics that distinguish one substance from another are called properties. A physical property is a characteristic of matter that is not associated with a change in its chemical composition. Familiar examples of physical properties include density, color, hardness, melting and boiling points, and electrical conductivity.

General, specific properties are common to all matters online
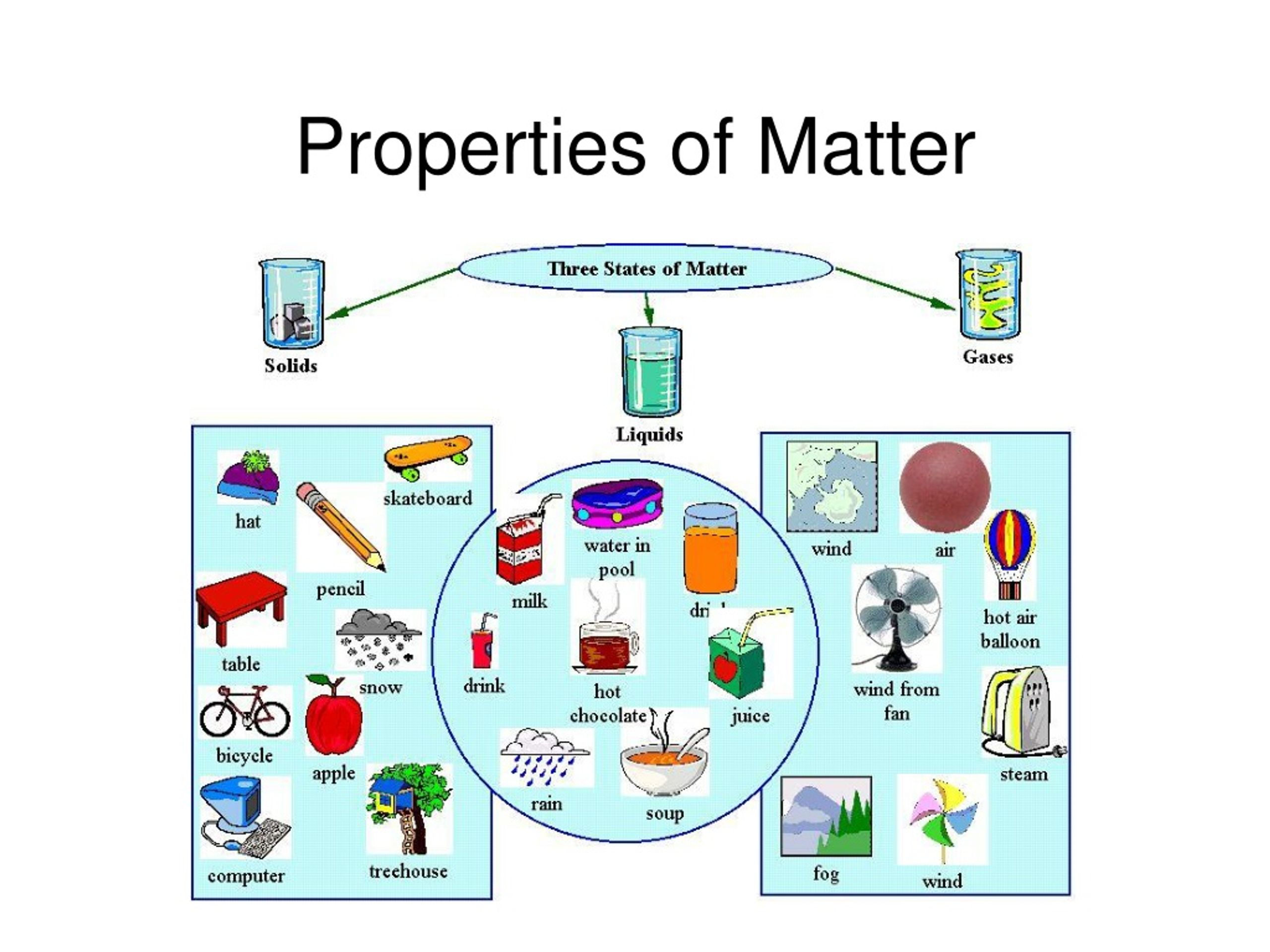
Plasma is the fourth state of matter which is similar to an ionized gas. It contains mostly free electrons and positively charged ions, which are left behind when one of these particles leaves its charge center. Water is a substance that can exist in 3 of the 4 states of matter. It can be a liquid (regular water), solid (ice), or gas (steam).
Properties of Matter Science 6 at FMS
Physical changes are related to physical properties since some measurements require that changes be made. The three main states of matter are: Solid, Liquid, Gas. Solid is distinguished by a fixed structure. Its shape and volume do not change. In a solid, atoms are tightly packed together in a fixed arrangement.
Properties of Matter Review Quizizz
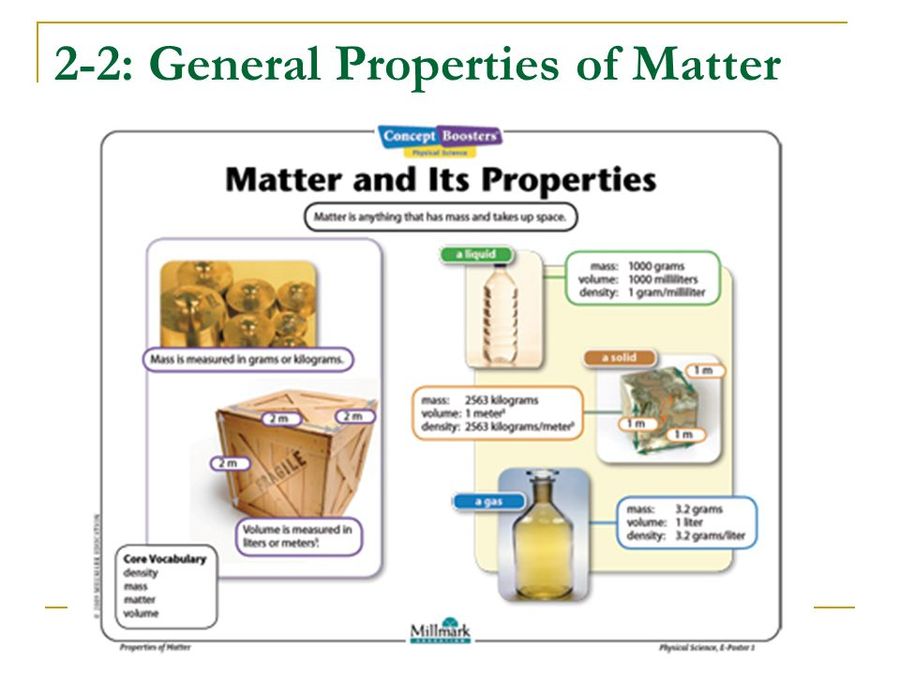
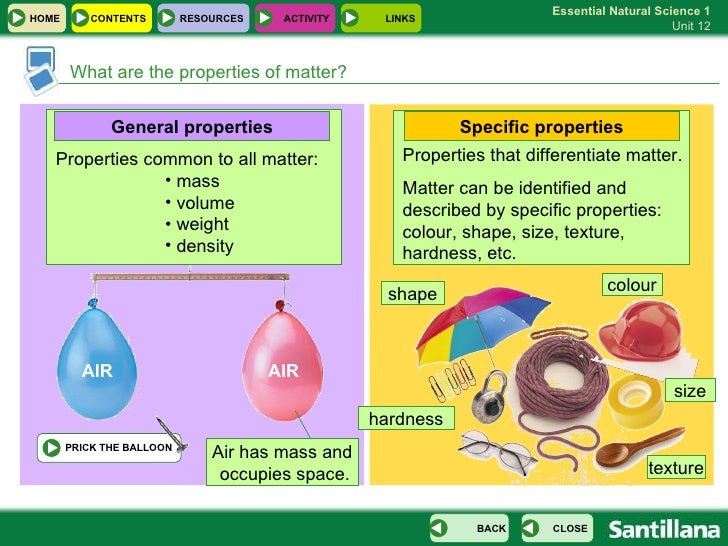
Properties are the traits that allow us to differentiate one material from another. The matter is a physical substance that takes up space, has mass, is made up of atoms, and can be converted into energy.In this article, we will look at the various properties of matter, the importance of the properties of matter and how these properties of matter are defined and calculated.
U12 MATTER AND ITS PROPERTIES
matter, material substance that constitutes the observable universe and, together with energy, forms the basis of all objective phenomena. At the most fundamental level, matter is composed of elementary particles known as quarks and leptons (the class of elementary particles that includes electrons ). Quarks combine into protons and neutrons.

General Chemistry Q1 Mod1 PropertiesofMatter 11 General Chemistry
What is the difference between General Properties and Special Properties of Matter?

ConceptMap Chemistry education, Properties of matter, Interactive
Samantha Ma (UC Davis) 1.3: Properties of Matter is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. All matter has physical and chemical properties. Physical properties are characteristics that scientists can measure without changing the composition of the sample under study, such as mass, color,..

General, specific properties are common to all matters online
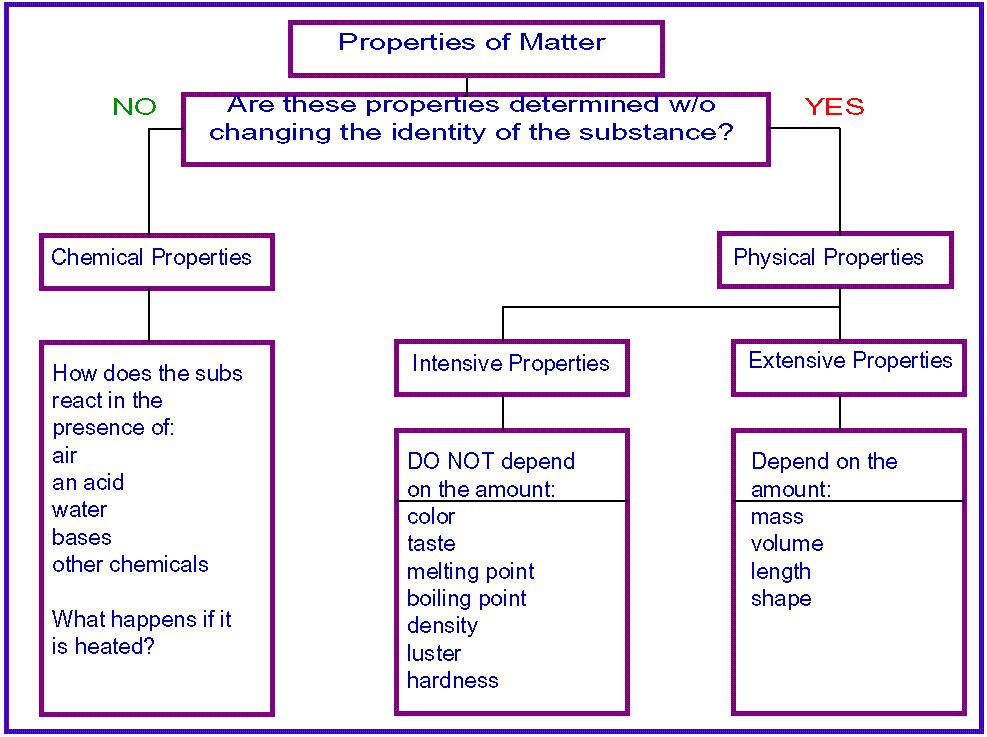
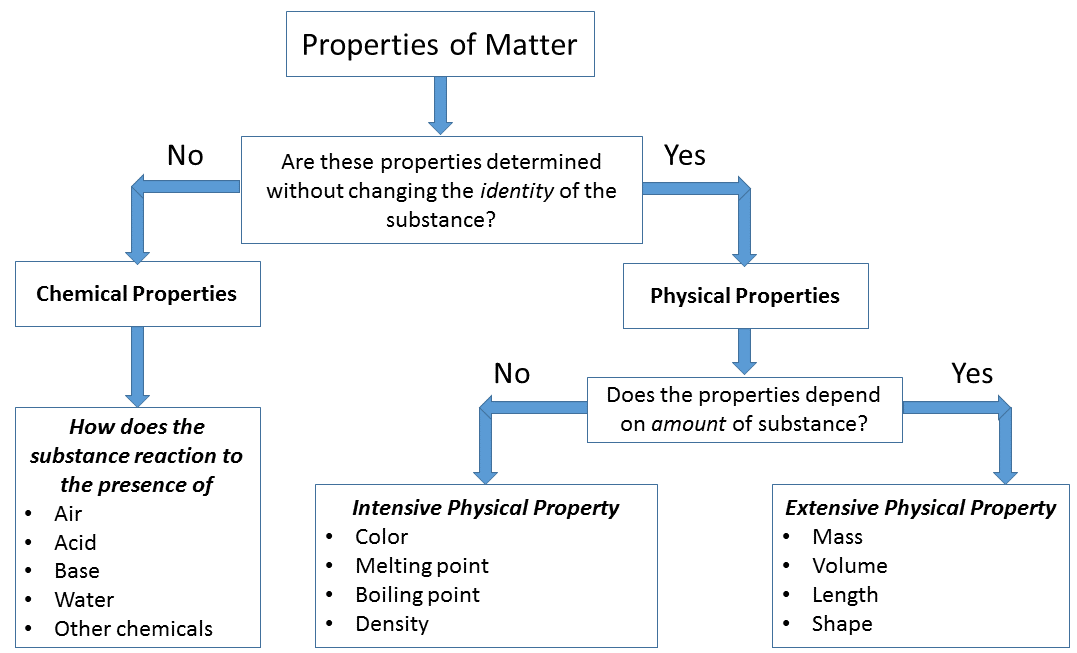
physical property: Any characteristic that can be determined without changing the substance's chemical identity. chemical property: Any characteristic that can be determined only by changing a substance's molecular structure. All properties of matter are either extensive or intensive and either physical or chemical.
/chemical-properties-of-matter-608337-v33-5b6334d346e0fb0082054666.png)
Chemical Properties of Matter
Some properties, such as mass and volume, depend on the quantity of matter in the sample we are studying. Clearly, these properties, as important as they may be, cannot by themselves be used to characterize a kind of matter; to say that "water has a mass of 2 kg" is nonsense, although it may be quite true in a particular instance.

PPT Matter, Elements & Atoms PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Specific properties of matter are those properties that can be used to identify a substance. Examples: BOILING POINT - It is the temperature at which a substance undergoes the change of state from liquid to vapour.. MELTING POINT-It is the temperature at which a substance undergoes the change of state from solid to liquid.. DENSITY - It is the ratio between mass and volume.
Chemistry Ch.5 Properties of Matter Mr.Panchbhaya's Learning Website
All matter has certain properties that define it. There are six major physical properties. In order for us to measure or observe them, we do not need to change the composition of the substance. The six physical properties are color, density, volume, mass, boiling point, and melting point. Chemical properties are those which we can measure only.

Specific properties of matter hardness, elasticity, transparency
The fundamental properties that we use to measure matter in are; Inertia, Mass, Weight, Volume, Density and Specific Gravity. The periodic table is a visual method of interpreting the chemical properties of elements which effect the measurements below.. These measurements can be classified into two categories, intrinsic and extrinsic.

Chapter 1 Measurements in Chemistry Chemistry
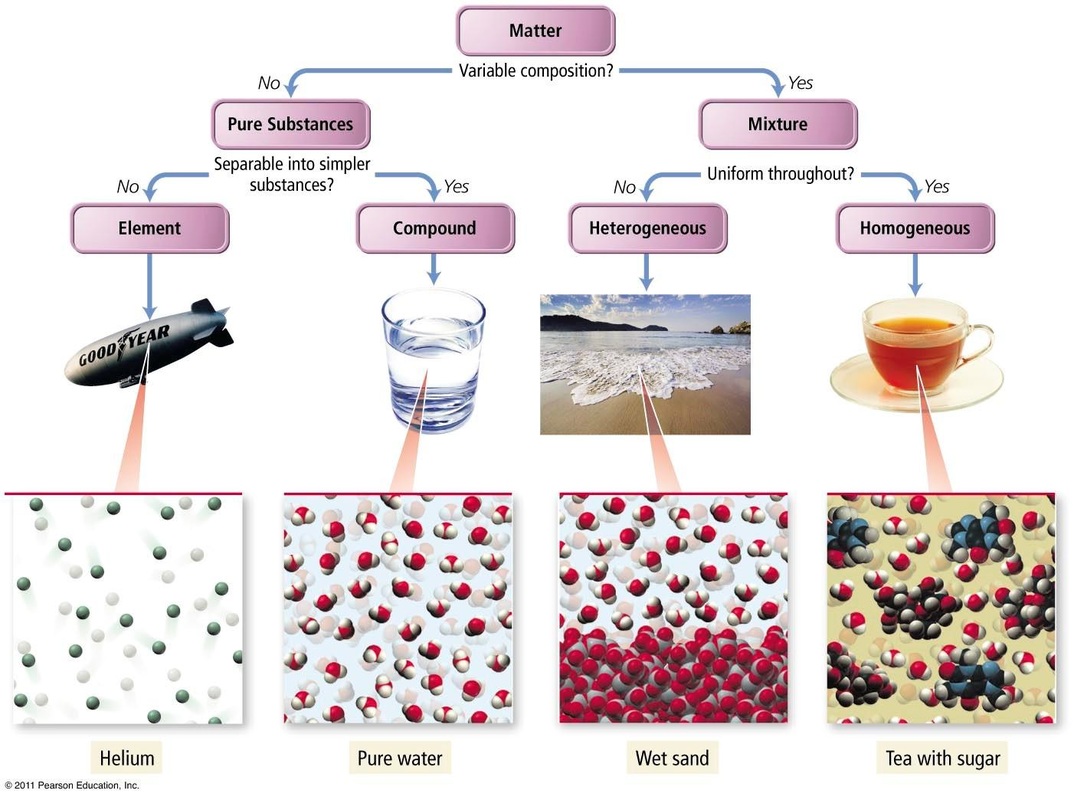
A phase is a region of matter that possesses uniform intensive properties throughout its volume. A volume of water, a chunk of ice, a grain of sand, a piece of copper— each of these constitutes a single phase, and by the above definition, is said to be homogeneous. A sample of matter can contain more than a single phase; a cool drink with ice.
What is matter? CHEMISTRY 9
The properties that chemists use to describe matter fall into two general categories. Physical properties A charactristic that describes matter, such as size, shape,. represent the three phases A certain form of matter that includes a specific set of physical properties. of matter. A solid has a definite shape and a definite volume.
- A Teatro Con Gianni Rodari Pdf
- Fragmento De Una Obra De Teatro Del Siglo De Oro
- Rastreo De Dinero Western Union
- Advanced Systemcare V 12 1 0 Clave A Pro
- Cuanto Tiempo Queda Para El Evento De Fortnite
- Consejo De Defensa De La Nacion
- Pisos En Alquiler Baratos En Galapagar
- American Family Insurance Emergency Road Service
- Que Piedra Es De Piscis
- Que Es Un Solenoide De Transmisión Automática