
Amprobe SM10 Sound Meter with A and C weighting TEquipment
To answer your question, it is not C but A weighting that "gives an approximation of the actual response of the human ear, as determined by Fletcher Munson."-Yamaha SOundreinforcement handbook. However, once you get past 100 db the ear's frequency response becomes more linear so C weighing would be more appropriate from this SPL up.

compassasrpos Blog
C-weighting is optimized for full-bandwidth sources at levels exceeding 85dB. A-weighting filters out the high and low frequencies and is optimized for lower volumes. Gibson, Bill. p.46 The Ultimate Live Sound Operator's Handbook. 2nd ed. Milwaukee: Hal Leonard, 2011. Pro audio equipment often lists an A-weighted noise spec − not because it.

Difference between A, B and C sound weighting curves YouTube
The most common weighting that is used in noise measurement is A-Weighting. Like the human ear, this effectively cuts off the lower and higher frequencies that the average person cannot hear. Defined in the sound level meter standards (IEC 60651, IEC 60804, IEC 61672, ANSI S1.4), a graph of the frequency response can be seen to the right.

Add Sound Production
A C-A measurement of 10 dB at 100 dBA means that the total C-Weighted energy is reaching 110dB C. When the C-A measurement is 20 dB or more in a live music environment, it's quite possible that the SPL of the lower frequencies could be dangerously high, especially if the A-Weighted measurement is 100 dB or more.

FT3432 Hioki, Sound Level Meter, 30dB to 137dB, A weighting or C
Frequency-Weighting Sound Level Measurements: A-weighting dB (A) vs. C-weighting dB (C) Most sounds can contain a mixture of many frequencies simultaneously. The human ear varies in its sensitivity to sounds of different frequency. Therefore, sound levels are often measured using a frequency-weighted filter which emulates the frequency.

Sound Level Meters
The C-weighting network is used mainly as a measure of the broadband sound pressure level as well as for recording. Occasionally an (L C − L A) level is used to describe the relative contribution of low-frequency noise to a spectrum. The weightings can be applied to sound power or sound pressure levels.

Sound Level Meter TA060 1 Year Warranty Sealey
The A-weighted sound level discriminates against low frequencies, in a manner similar to the response of the ear. In this setting, the meter primarily measures in the 500 to 10,000 Hz range. It is the weighting scale most commonly used for OSHA and DEQ regulatory measurements. The C-weighted sound level does not discriminate against low.
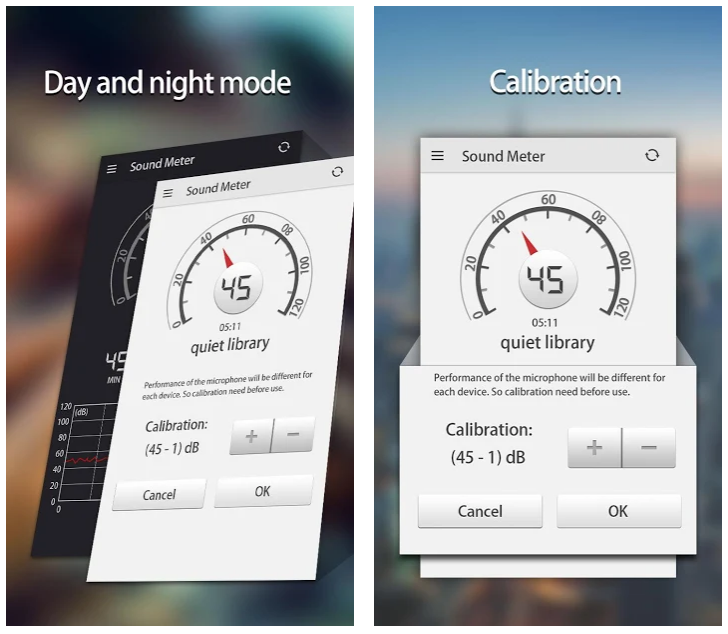
5 Best Noise Level Apps for Android
C-weighting is less severe on low frequencies than A-weighting and represents the response of the human ear to loud sounds (over 100 dB). C-weighting is more typical of machine noise and jet noise measurements than in other acoustics applications. All Class 1 sound level meters are mandated to allow for C-weighting. D. D-weighting, like B.

AudioStryke Portable Decibel Meter with MAX Data Hold, LCD Display
Look for labels such as dB(C), C, dBC, LCeq, LCPeak, or LCE. LPeak, or Peak Sound Pressure, shows as LCPeak. Z Frequency Weighting 'Z' stands for zero; this weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 Hz and 20,000 Hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise.
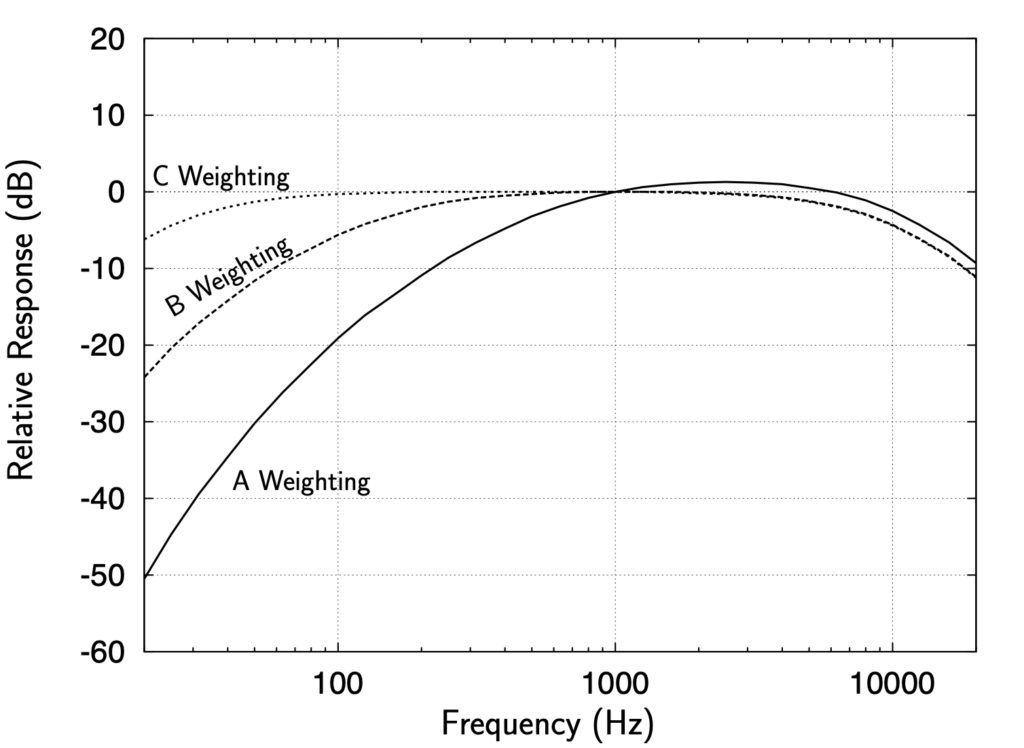
Engineering at Alberta Courses » Psychoacoustics and Weighting Networks
The C-weighted frequency looks more at the effect of low-frequency sounds on the human ear compared with the A-weighting and is essentially flat or linear between 31.5Hz and 8kHz, the two - 3dB or 'half power' points. Peak Sound Pressure Measurements are made using the C- frequency weighting. This is c-weighted peak is for measuring.

Weighting Filters
This video explores the difference between A-weighted and C-weighted decibels.Learn more about live sound at:https://www.theproductionacademy.com/coursesOne.
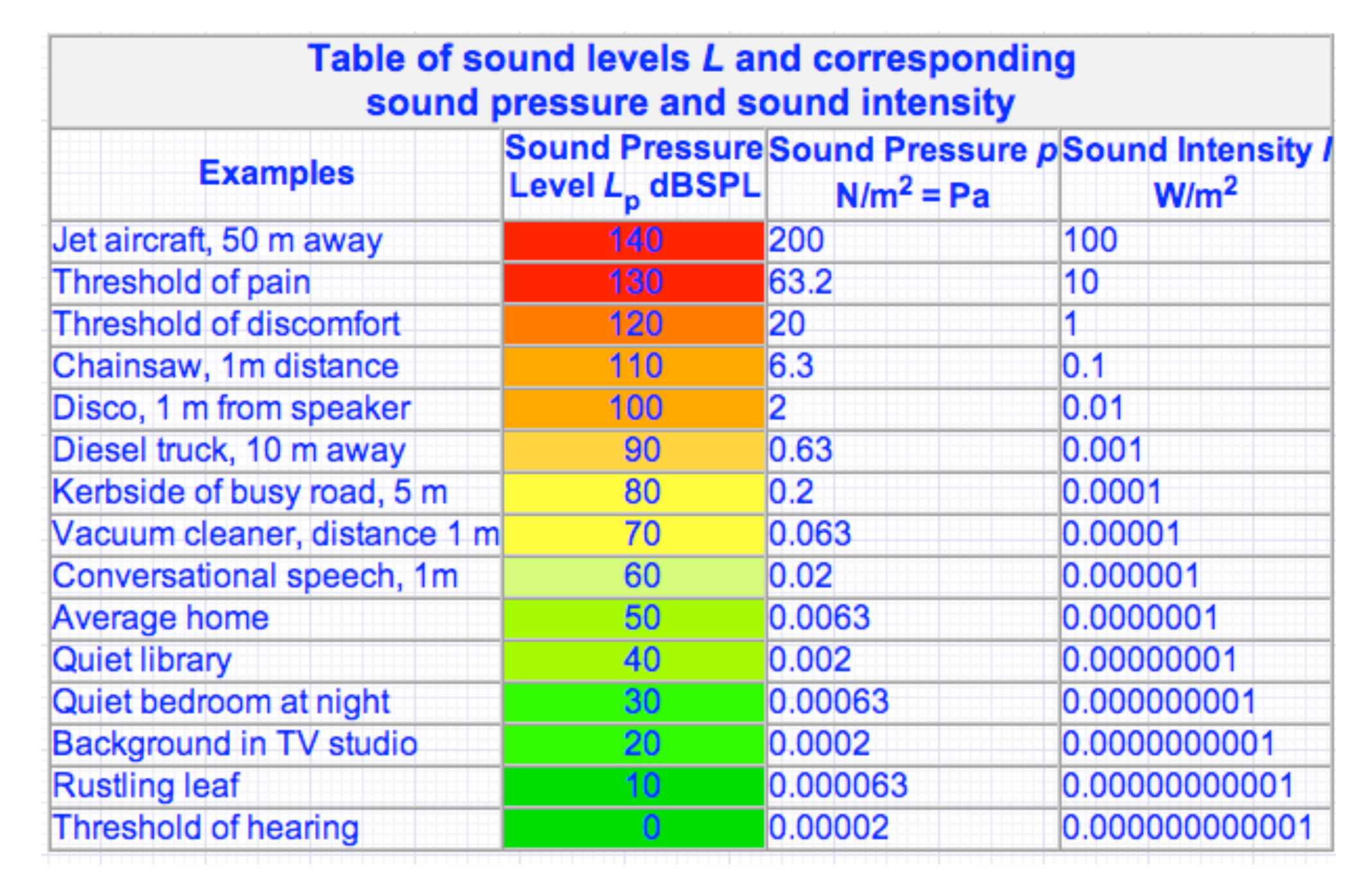
Decibel Conversion Chart
The A and C weightings are thus most meaningful for describing the frequency response of the human ear toward real world sounds. As acoustic sound level measurements are often motivated by the effect of sounds on humans, the A-weighting filter is commonly applied. The C-weighting filter is often applied when representing peak levels.

How to use a custom weighting curve in Smaart® and why I don’t
A-weighting and the spectrum of live sound A-weighting is the most widely used frequency weighting for sound level measurements. Established risk criteria for noise-induced hearing. C-weighted sound level limit; and • obtaining reliable measurements of low-frequency sound levels can be challenging, particularly in small indoor venues.
Frequency Weighting
The C-weighted frequency looks more at the effect of low-frequency sounds on the human ear compared with the A-weighting and is essentially flat or linear between 31.5Hz and 8kHz, the two - 3dB or 'half power' points. Peak Sound Pressure Measurements are made using the C- frequency weighting. This C-weighted peak is for measuring impulse.

Auto Measuring A and C weighting network selection 30130dB Sound Level
The most used frequency weightings you will see on a modern sound level meter, or noise dosimeter are 'A', 'C' and 'Z'. The Cirrus Optimus Sound Level Meters will measure all three frequency weightings at the same time, saving you the risk of measuring the wrong parameter. 'A' Frequency Weighting. This is the standard weighting.

Propensity Score Weighting Using Generalized Boosted Models — method
For example, a sound at 1000 Hz at 80 dB SPL appears to sound as loud as a 100 Hz sound at 90 dB SPL. Read more about the equal loudness curve here and here. A-weighting measures sound as if it's heard by the human ear. This weighting reduces frequency volume below 600Hz.
- Piedra Papel Tijera Juego Online
- Donde Vender Oro Al Mejor Precio En Madrid
- Ejercicios En Los Que Se Practique Voleibol
- Recambios Ejes Y Cajas Sa
- Los Puentes De Madison Hd
- Master Gestion Cultural Universidad Complutense
- Estanque De Agua Seccion Constructiva
- 5 Htp Hydroxytryptophan Complex Solgar Indicaciones
- A Que Hora Iluminan El Puente Luis 1 En Oporto
- Como Conseguir Ala Plateada En Pokemon Soul Silver